|
교신저자:장철호, 570-060 전북 익산시 신용동
전화) (063) 850-1311, 전송) (063) 841-6556, E-mail) chul@wonnms.wonkwang.ac.kr
서
론
어지러움증을 주소로 하는 말초성 전정 질환중 많은 빈도를 차지하는 급성 전정신경염은
30~50대에 걸쳐 높은 비율로 나타난다. 급성 전정신경염의
원인으로는 바이러스 감염이 주 원인으로 여겨지고 있으며 대다수 환자에서 상기도 감염 또는 Ramsay-Hunt 증후군, 이하선염 등을 동반하는
것으로 알려져 있다.1)2)
최근 전정와우 질환의 진단에서 자기공명영상은 Gadolinium-diethylenetriamine pentaetic acid(Gd-DTPA)를
사용함으로써 진단적 민감도가 커져 많이 사용되고 있다.
바이러스 감염이 원인으로 알려진 벨마비에서는 Jonsson 등3)이 진단적 유용성을 보고한 이래 국내에서도
Cha 등,4) Lee 등5)에 의해서 환자 대다수에서 안면신경의 조영증강이
나타났으며 병변의 위치를 아는데 도움을 준다고 보고되었다. 그러나 바이러스 감염이 주원인으로 알려진 급성 전정신경염에서 자기공명영상의 조영증강에
대한 연구 보고는 거의 없는 편이다.
본 연구의 목적은 급성 전정신경염에서 자기공명영상이 병변 위치 파악에 도움을 주는지 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
1997년부터 1999년 12월까지 급성 전정신경염으로 내원하여 치료하였던 환자들 중 자기공명영상을 시행하였던 17례의 환자들을 대상으로
하였다. 연구대상의 남녀 비율은 1:1.2였으며 평균 나이는 47세였다. 자기공명영상에서 조영증강이 나타나는 빈도, 위치를 조사하고 대조군으로는
직접적인 원인을 찾지 못하여 벨 마비로 진단 받고 자기공명영상을 시행했던 환자 20례을 대상으로 하였다.
자기 공명 영상은 4 mm 두께 image로 Sigma 1.0 T(Simens, Magnetom 42SP, Germany)를 사용하였다.
조영제로 Gd-DTPA를 이용하였으며 용량은 0.2 cc/kg를 정맥 투여하였다. 사진의 판독은 방사선과 전문의와 함께 T1 강조 영상에서
Gd-DTPA 투여전과 투여후 사진을 대상으로 전정와우, 미로를 판독하였다.
결 과
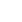
내원했던 환자들은 전정신경염 증상이 발현된지 7일부터 30일 이내였으며 그 사이에 자기공명영상을 시행하였다. 전정 신경염 17례 전례에서
전정신경, 미로에 조영 증강이 전혀 나타나지 않았다(Fig. 1). 그러나 대조군인 벨 마비에서는 20례 환자중 19례에서 명확하게 안면신경이
조영되었으며 1례에서는 조영증강이 나타나지 않았다.
고 찰
바이러스 감염이 주 원인으로 알려진 벨 마비에서는 Gd-DTPA을 이용한 자기공명영상을 시행해 왔다. 차 등3)의
보고에 의하면 17례중 15례에서 모두 병변 쪽에서 조영증강이 되었으며, 병변 반대 쪽은 모두 조영증강이 되지 않았다고 하였으며 저자들의
경우 20례에서 19례에서 조영증강이 되었다.
Kenneth 등6)에 의하면 Gd-DTPA을 사용한 자기공명영상은 paramagnetic 물질로 T1 relaxation
time을 짧게하여 조영증강을 나타낸다. Gd-DTPA는 정상적으로는 뇌혈장막을 통과하지 못하기 때문에 5, 7, 8 뇌신경의 cistern
부위는 조영증강이 되지 않는다. 벨 마비에서 조영증강되는 이유들은 조직의 부종, 염증, 또는 종물에 의한 외세포액의 증가 때문이라고 설명할
수 있다.7)8) 벨마비는 염증이 심할수록 조영증강이 잘되고 안면신경의 모든
분절에서 관찰되며 주로 내이도 분절의 원위부와 미로분절, 슬상신경절 및 고실분절에서 나타난다. Cha 등4)은
17례중 15례에서, Lee 등5)은 19례중 16례에서 조영증강이 나타났으며 저자들의 경우 20례에서 19례에서
조영증강이 되었다.
일반적으로 전정와우 신경이나 미로에 조영증강이 되는 경우는 벨마비 외에도 herpes zoster oticus, 바이러스 내이염, Cogan
증후군 등이다. Herpes zoster oticus는 전정와우 신경이나 미로에 병변을 일으키며 혈액-신경 장막(blood-nerve barrier)의
파열이나 파괴를 유발하여 조영증강이 되는 것으로 알려져 있으며 전정와우 증상과 안과적 증상을 일으키는 급성 자가면역질환으로 알려진 Cogan
증후군도 급성 미로염을 일으켜 조영증강이 일어나는 것으로 보고되었다.9)
최근의 연구에 의하면 herpes simplex virus I의 DNA가 인체 측두골의 전정신경절에서 중합연쇄반응검사를 통해 밝혀지면서,
전정신경염은 벨마비처럼 latent herpes virus의 재활성화로 추정되고 있다.10)
본 연구에서는 전정신경염 전례에서 조영증강이 나타나지 않았다. 이는 Hasuike 등의 결과와 일치하였다.11)
벨마비에서는 조영 증강이 일어나지만 전정신경염에서 조영증강이 일어나지 않은 이유로는 안면신경과 전정신경의 동정맥 구조(arteriovenous
structures)의 차이로 생각되고 있으며 안면신경은 신경 둘레의 동정맥 구조가 풍부하기 때문에 벨마비에서는 동정맥 구조에 충혈로 인해
조영증강이 잘 나타난다고 설명되었다.11)
전정신경염에서 조영증강이 나타나지 않은 이유들로는 이러한 동정맥
구조의 차이외에도 벨마비보다는 경한 바이러스의 재활성으로 인해 조영 시 확실히 보일 수 있는 역치를 넘지 못하기 때문이며, 급성이라기 보다는
아급성 재활성으로 생각되고 있기 때문이다.11)
그러나 아직 정확한 이유는 알수가 없어 이에 대한 추가적인
연구들이 필요한 실정이다.
결 론
급성 전정신경염에서는 자기공명영상 T1에서 Gd-DTPA 조영증강이 나타나지 않아 전정신경염의 병변 부위를 파악하는데는 도움이 되지 못했다.
REFERENCES
-
Schuknecht HF, Kitamura K.
Second Louis H. Clerf Lecture,
Vestibular neuritis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1981;suppl 90:1-19.
-
Longridge NS. Recurrent vestibulopathy: Support for a viral
etiology. J Otolaryngol 1989;18:99-100.
-
Jonsson L, Tien R, Engstrom M, Thuomas KA. Gd DPTA enhanced
MRI in Bell's palsy and herpes zoster oticus: an overview and implications for
future studies. Acta Otolaryngol(Stockh) 1995;115:577-84.
-
Cha CI, Seok SR.
Gadolinium-enhanced MRI findings of Bell's
palsy and Herpes zoster oticus. Korean J Otolaryngol 1993;36:498-505.
-
Lee HK, Moon Sw, Lee JJ, Choi JY, Kim TM, Kim SG, et al.
Clinical
implication of magnetic resonance imaging in Bell's palsy. Korean J Otolaryngol
2000;43:24-8.
-
Kenneth K, Steven M, Wayne K.
Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic
resonance imaging in facial nerve lesions. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1990;102:26-33.
-
Daniels DL, Caervionke LF, Millen SJ.
MR imaging of facial
nerve enhancement in Bell's palsy or after temporal bone surgery. Radiol Arch
Otolaryngol 1989;171:807-9.
-
Millen SJ, Daniels DL, Meyer GA.
Gadolinium enhanced magnetic
resonance imaging in temporal bone lesions. Laryngoscope 1989;99:257-60.
-
Casselman JW, Majoor MH, Albers FW.
MR of the inner ear in
patients with Cogan's syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1994;15:131-8.
-
Furuta Y, Takasu T, Fukuda S, Inuyama Y, Sato KC, Nagashima
K. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 in human vestibular ganglia. Acta Otolaryngol
(Stockh) Suppl 1993;503:85-9.
-
Hasuike K, Sekitani T, Imate Y.
Enhanced MRI in patients
with vestibular neuronitis. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) Suppl 1995;519:272-4.
|

 PDF Links
PDF Links
 Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI
 Download Citation
Download Citation