|
 |
- Search
| J Audiol Otol > Volume 24(2); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Several novel animal models that represent the pathophysiological process of endolymphatic hydrops (ELH) of Meniere’s disease (MD) have been developed. Animal models are important to identify and characterize the pathophysiology of ELH and to corroborate molecular and genetic findings in humans. This review of the current animal models will be useful in understanding the pathophysiology of and developing proper treatments for MD. Surgical animal models will be replaced by medication-induced animal models. Study models previously developed in guinea pigs will be developed in several smaller animals for ease of conducting molecular analysis. In this review, we provided updated resources including our previous studies regarding the current and desirable animal models for MD.
Meniere’s disease (MD) is a well-known inner ear disease characterized by symptoms of recurrent vertigo lasting for hours and fluctuating hearing loss with tinnitus or ear fullness [1]. The prevalence has been estimated as 190 per 100,000 people in the United States, increasing markedly in the elderly [2]. Endolymphatic hydrops (ELH) has been postulated to be the pathological origin of MD [3,4], as structures bounding the scala media by the Reissner’s membrane are enlarged into the scala vestibuli. Although the association between ELH and MD is well known, the mechanism through which ELH produces symptoms and its association with the progression or treatment of MD remain unknown. Animal models of ELH could provide a basic scientific understanding of MD [5], and because the first model (with surgical obliteration of endolymphatic duct for ELH) was the guinea pig [6], considerable methods have been introduced to develop an appropriate animal model for MD.
According to Salt and Plontke review [3], either acute or chronic models were classified as models of ELH. Acute models could be created by cerebrospinal fluid pressure manipulation, injection into the scala media, stimulation of low frequency sound, or gel injection into the cochlear apex. For the creation of chronic ELH models, surgical ablation of the endolymphatic sac (ES) or systemic medication such as aldosterone, systemic vasopressin (VP), or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were used in vestibular research. These animal models introduced for ELH till date show the dilation of the scala media with low frequency hearing loss; however, they do not exactly reflect the fluctuating hearing loss or vertigo characterized in patients with MD [7]. Because they were developed for ELH research 10 years after the review, the comparison of animal models will provide enough background to reflect the molecular and cellular pathophysiologies occurring in the ELH of the inner ear. In this review, we divided the currently available animal models into different types to resemble the pathophysiology of MD, and we outlined some of the more recently used methods.
Research on MD faces several significant challenges. The inner ear system is highly complex; the cochlear and vestibular organs are connected, and the extent of involvement in each organ varies, resulting in hearing loss or equilibrium disorders. Since the pathophysiology of MD has not yet been elucidated, and no accurate objective diagnosis method has been provided, it is difficult to generate an animal model that accurately reflects the disease. Previous ELH models, such as the ‘‘endolymphatic sac ablation’’ model [8] and the ‘‘systemic vasopressin’’ model [9,10], are not representative of acute attacks of MD, because they can only represent the chronic end stage of disease with permanent hearing loss and vestibular dysfunction. It is also necessary to develop a method for the quantitative analysis of the changes in vestibular function before and after an acute attack of hydrops, as well as imaging.
The ablative surgery of the vestibular organ could be performed occasionally among patients diagnosed with intractable MD or temporal bone tumors. In addition to the complexity of the inner ear, any molecular-chemical analysis of the inner ear is compromised because the removal of intact human cochlear and vestibular organs for functional characterization, even post-mortem, is difficult as it is embedded within the hardest temporal bone in the body [11]. This unavailability of the membranous labyrinth from the human inner ear has caused hearing research to lag [12]. There are many technical difficulties in processing the human temporal, which keep hair cells in the cochlear and vestibule intact bone, to preserve the morphology. The need for animal models of ELH to apply the molecular and genetic findings of human inner ear are of the utmost importance.
The cochlea, a coiled bony structure approximately 35 mm long, has three chambers: scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani. The membranous labyrinth in the cochlea includes the scala media containing the endolymphatic fluid. The role of ES in the cochlea is well recognized as fluid absorption for endolymphatic homeostasis [13]. ES with the layers of dura mater is connected to the endolymphatic duct placed within the bony vestibular aqueduct. ES removes the endolymph via longitudinal flow. The euvolemic state of the endolymph has an important role for endolymph homeostasis. The endolymphatic volume allows ion homeostasis such as potassium in the endolymph through the microstructures of spiral vascularis and sensory hair cells [14]. The use of a systemic β-adrenergic agonist such as isoproterenol increases endolymph pressure and decreases lumen potential of ES. Salt and Plontke [3] showed that after sac ablation, the effects of isoproterenol on endolymph pressure and electrolyte potential were suppressed. Surgical destruction, or the addition of an immune mediator to the ES, has been successfully used in guinea pigs to generate animal models. Immunoglobulins such as IgG, IgM, and IgA have been found in ES [15]. An immune reaction from these components of the immune system may induce inflammation in the inner ear and disturb the circulation of endolymphatic fluid. Schuknecht and Gulya [16] suggested that the Reissner’s membrane rupture (potassium rich endolymph) secondary to endolymphatic duct distention was responsible for the clinical manifestation of MD. Toxicity due to a potassium influx into perilymph on hair cell and spiral ganglion could cause episodic vertigo and result in long-term impairment in hearing and vestibular function. The cochlear hydrops usually dilatates the Reissner’s membrane toward the scala vestibuli. Saccular hydrops, the second most common site next to cochlear hydrops, might distend into the stapes footplate, inducing stapedial fixation. The abnormal function of other microstructures of the membranous labyrinth may be involved in development of ELH. The obstruction of the endolymphatic duct may result in distention of ELH, leading to potassium rich endolymph [14]. The endolymphatic sinus is well known as an endolymph volume regulator by detecting even minor changes in endolymph pressure compared to that of perilymph [17]. Thus, dysfunction of ES might increase endolymph, and displaced sinus walls into the ES might occlude the opening of endolymphatic ducts [3].
Endolymph homeostasis can be affected by various hormones. Indeed, studies on antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, the aquaporin system, and ion channels demonstrated associations with the pathophysiology of MD. ADH, which acts on the vasopressin-2 receptor (V2R) related with aquaporin-2 channels (AQP-2), suppresses water reabsorption in ES, resulting in ELH. Aoki, et al. [18] reported a significant increase in ADH concentration during a Meniere’s attack. V2R has been expressed at high concentrations in ES of the human inner ear. Kitahara, et al. [19] demonstrated that mRNA expression of V2R in ES is upregulated in patients with MD. Because high potassium in the scala media plays the most important role in the generation and maintenance of the endocochlear potential, epinephrine, a modulator of potassium secretion by marginal cells, affects the increase of endolymph volume in and the dilation of the intraosseous portion of the sac [20]. The systemic dosing of aldosterone also increases the rate of endolymph production, leading to an increase in Na-K ATPase levels in the lateral wall of the cochlea [2].
A recent study demonstrated that airborne and food allergies were found in 59.2% and 40.3% of patients with MD, respectively [21]. It is thought that circulating antigens or immune complexes can enter the periphery of ES and fenestrated blood vessels, stimulating mast cell degranulation. Histamines, known as vasoactive mediators, can make blood vessels of the sac pharmacologically vulnerable [15]. Circulating immune complexes in MD patients were reported, varying from 21% to 96% [22]. Endothelial injury due to elevated complexes increases the permeability of the capillaries surrounding the ES, and this results in acute ELH or rupture of the Reissner’s membrane [23]. The application of LPS to the scala media is known to induce a severe immune reaction in the inner ear. We demonstrated that an immune challenge of the cochlea using LPS can lead to moderate-to-severe hearing loss and confirmative ELH in guinea pigs [24].
Genetic predisposition is observed in 2.6-12% of patients with MD [25]. Though several studies have identified human leukocyte antigen associations, none have been proven [25]. Teggi, et al. [26] showed that adducin changes can increase Na-K ATPase activity, and induced hyperosmolarity in the scala media might result in pathologic hydrops. Furthermore, the PTPN22 1858C/T genotype can provide differential susceptibility to bilateral MD [27], whereas it has been reported that the longer alleles of (CA)17-20 poly (ADP-ribose)-polymerase 1 (a nuclear enzyme that contributes to both neuronal death and survival under stress conditions) and host cell factor C1 on the X chromosome haplotype block (related to herpes virus replication within neurons) are protective against bilateral MD [27].
Surgical animal models accurately reflect the pathology of MD progress by showing dilatation of the scala media. In 1965, Kimura and Schuknecht [6] created an ELH model in a guinea pig via surgical ablation of the endolymphatic duct and ES by electrocauterization. The prolonged malabsorption of endolymph induced by ablation of ES led to the development of ELH. Many investigators followed this surgical procedure because it reliably produces the histological dilatation of ELH and moderate-severe hearing loss in a chronic phase. The original intradural technique had limitations of significant surgical morbidity and intensive animal care. Dunnebier, et al. [28] developed mild ELH by completely removing the extra-osseous part of ES (extradural technique) around the sigmoid sinus. The obstruction of venous outflow to the sigmoid sinus might induce fibrosis in the most distal portion of the ES. Although studies with surgical models of guinea pig have provided valuable insights into the pathophysiology of ELH, they only showed that secondary ELH was different from spontaneous ELH. In secondary ELH, ES is non-functional, and fluctuating vestibular symptoms were also not reproducible [24].
In addition to inducing hydrops in animals with surgical sac ablation, there have been some attempts for combining medication with the surgical removal of ES. By enhancing secretion of K+ into endolymph, aldosterone with partial sac ablation may exacerbate the dysfunction of endolymphatic circulation in a few animals. Egami, et al. [29] suggested injecting the modified surgical animal model with additional desmopressin to accelerate the development of ELH. The guinea pig model with an injection of desmopressin 1-4 weeks after the ablation of ES showed episodes of imbalance along with spontaneous nystagmus. Because the water homeostasis of the inner ear fluid is partly regulated by the VP-AQP-2 system, desmopressin (V2R agonist) was used in the animal model for ELH to examine V2R effects of VP in the inner ear. However, surgical ablation could be not a straightforward model of ELH because MD patients have an intact ES [30] and surgical ablation of animal models was still not physiologically a case of MD; it was also destructive. Although they showed acute moderate-severe hearing loss and histologic change of hydrops, these surgical animal models did not show episodic vestibular symptoms or fluctuating hearing loss.
To compensate for the problems of surgical ablations, “overproduction” models have been developed with long-term administration of VP or aldosterone, injection of cholera toxin, and various methods to induce autoimmune disease in the inner ear. V2R, which regulates water movement by controlling the expressions of the aquaporin channel, has been found in inner ear tissues, including the lateral wall and ES [29,30] (Table 1). ES of patients with MD have higher levels of VP receptors as well as levels of systemic VP. Takeda, et al. [9] administered OPC-31260 (V2R antagonist) at 400 μU/kg/ min and 1,000 μU/kg/min (high concentrations) for 1 week using an osmotic mini-pump in guinea pigs as a model for hydrops. The administration of OPC-31260 into the cochlea could aid in recovery of ELH caused by ES ablation [31]. Compared to the guinea pig, mice certainly have several advantages as a future animal model in inner ear research because a number of antibodies in mice are available and they provide more technical advantages for genetic investigation. The continuous administration of VP in C57BL6 and CBA/J strains of mice for MD was performed at a rate of 50 μg/100 g/day for 14-30 days without any surgery [31]. They initially reported the development of hydrops after more than 2 weeks. However, they did not show reversible vestibular dysfunction such as early irritable nystagmus or late paralytic nystagmus. Katagiri, et al. [32] succeeded in inducing ELH in CBA/J mice by injecting 1 mg LPS, which reduces the absorption of endolymph in ES, intratympanically once daily for 5 days and 100 mg/100 g/day aldosterone, which increases the production of endolymph, intraperitoneally for 5 days with an additional 1:10,000 epinephrine or 3% sodium nitroprusside, which reduces inner ear blood flow, 24 h after the last injection. They also reported that latanoprost, a selective agonist for the FP prostanoid receptor, might inhibit the development of ELH caused by VP.
Recently, some research used the dynamic immune system in the cochlea to induce an adaptive immune response in ES. LPS as a toxin extracted from Escherichia coli is well known to cause an immune response or inflammation in the inner ear. We had previously injected LPS directly into the scala media of guinea pigs and monitored functional and morphological changes over a period of 6 weeks [24]. We noticed severe ELH with minimal cellular infiltration in the cochlea following a 0.01% LPS injection that lasted at least 6 weeks (Fig. 1). Higher concentrations of 0.05% and 0.1% LPS could induce moderate-severe hearing loss and histological hydrops of ES, including endolymphatic duct with severe cellular infiltration. High concentrations of K+ in the endolymph fluid led to immune cell apoptosis in the scala media. Thereafter, a rapid efflux of K+ by LPS could increase the survival of immune cells in the scala media thereby clearing antigens.
Because rodents are similar to humans in terms of genetics, anatomy, and physiology as well as because of availability, ease of manipulation, and low cost, they are often preferred for hearing research. Since the introduction of X-linked hypophosphatemic studies in rickets, genetic defect models of PhexGy and PhexHyp with a non-functional phosphate-regulating gene and similar homology to endopeptidases located on the X chromosome (PHEX) might be studied for MD [33,34]. The target gene, encoding the PHEX protein, is a zinc-metalloendopeptidase located in the cell membrane of chondrocytes and osteoblasts to maintain the health of bone mineralization. Megerian, et al. [34] showed that the PHEX murine model (Hyp-Duk/Y) served as viable model to reproduce spontaneous, progressive hearing loss and vestibular impairment for MD.A positive relationship between the degree of ELH and hearing threshold was reported with an elevated summation potential/action potential ratio of electrocochleography (ECochG). Sheykholeslami, et al. [35] reported that compared to 10 adult normal mice (P60–P90), the Hyp-Duk/Y mice had either absent or elevated cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential (cVEMP) with a threshold of a 60 dB normal hearing level. Although the PHEX mutation is not seen in patents of MD, the PHEX murine model (Hyp-Duk/Y) certainly can serve as a viable mouse model that develops typical impaired hearing and balance symptoms for MD [36]. Future studies will enable the PHEX mouse to be a key animal model to hearing research for MD.
Several efforts have been made to visualize enlarged space of ELH via three-dimensional fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ECochG, cVEMP, and videonystagmography in animal models. However, the gold standard for diagnosis of ELH in animal models still remains confirmation of audiometry and histology after the section of cochlea. Because it is so difficult for animals to respond to the sound stimulation properly when checking hearing thresholds, the auditory brainstem response (ABR) has provided more qualitative and quantitative information for hearing thresholds, including the function of the auditory nerve and brainstem in the animal models [37]. The compound action potential (CAP; wave I of the ABR) is routinely used in hearing research [38,39]. We reported an abrupt recovery of CAP thresholds, SP/CAP ratio, cochlear microphonic distortion, and low-frequency modulated distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAEs) in the development of acute hydrops by injecting artificial endolymph into the scala media of guinea pigs [4]. Many reports in the literature state that ECoG is at least as sensitive as ABR [40].
Imaging technology, including MRI, might be developed as a critical tool for evaluating ELH in animal models for MD. In a recent study, ELH in mice was assessed using a high resolution 9.4 T field strength MRI [41]. Furthermore, light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) can be used as a means to obtain highly resolved 3D visualization of endolymphatic fluid movements; this has enabled researchers to examine the entire inner ear of experimental animals, en bloc, with subcellular resolution. We introduced fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran (FITC-dex) and artificial endolymph into the scala media of anesthetized guinea pigs via a glass micropipette (Fig. 2) [41]. When more than 2.5 mL of FITC-dex was injected into the scala media, FITC-dex was observed in the SSCs, utricle, and endolymphatic duct. The LSFM visually demonstrated the mechanism of endolymph volume regulation in patients with MD.
Our understanding about animal models will lead to scientific improvements in the development of treatments for MD. Animal models for ELH have provided us with a medium for studying the mechanical pathophysiology of hearing loss and vestibular dysfunction. Although surgical ablation of ES showed acute hearing loss and histologic changes of hydrops, they rarely showing episodic vestibular symptoms, which is a limitation of the procedure.
Further morphological and pathophysiological investigations for new animal models of MD need to be conducted. Though MD unfortunately remains an idiopathic disease, hydrops models in the fields of allergy, immunology, endocrinology, and genetics will provide multiple approaches for therapeutic options for patients with MD in the future.
Fig. 1.
Histopathologic images for endolymphatic hydrops in a new guinea pig model with immune reactions for Meniere’s disease by lipopolysaccharide at all time points (A-C: scala media, D-F: endolymphatic duct).
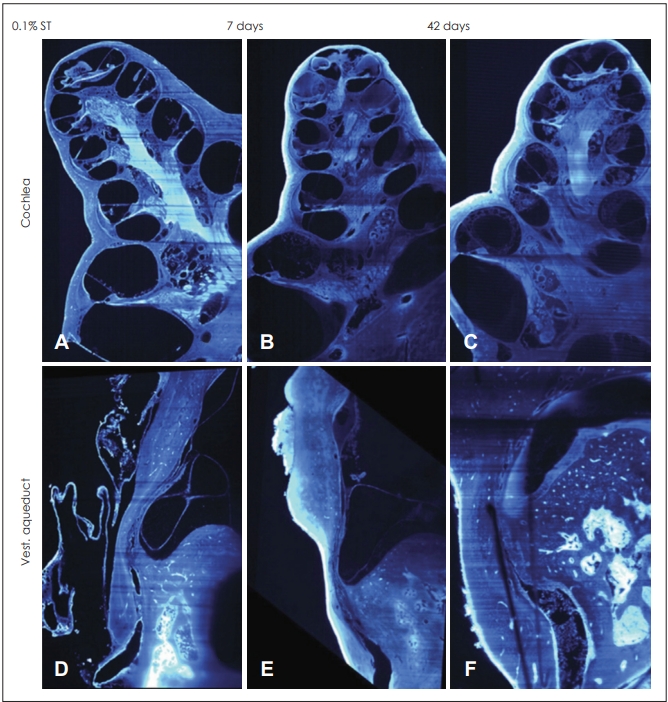
Fig. 2.
Visualization of endolymphatic space (blue color) by light sheet fluorescence microscopy after injecting fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran and artificial endolymph into the scala media in several views (A-G).
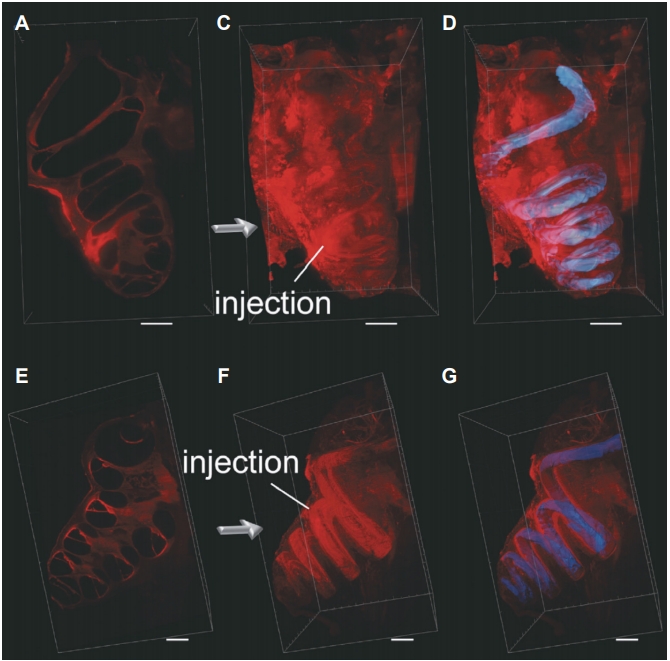
Table 1.
Animal models for Meniere’s disease by medication
| Reference |
Animal model |
Result |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Methods | Duration | Hearing symptoms | Vestibular symptoms | Histopathology | Etc. | |
| Brown et al. [24] | Guinea pig | LPS at 0.01%, 0.05%, or 0.1% in scala media | 6 w | >40 dB loss | None | 2-fold increase (0.1% LPS) | Compared by light-sheet fluorescence microscope |
| Egami et al. [29] | Guinea pig | Cauterized ES+100 mg/kg desmopressin | 1 w and 4 w | N/A | 100% spon. (1 w and 4 w) | ELH growth rate | Desmopressin (a VP type 2 receptor agonist)-AQP2 |
| 12.5%/h (1 w) | |||||||
| 23.7%/h (4 w) | |||||||
| Egami et al. [30] | Guinea pig | Cauterized ES+10 or 100 mg OPC-41061 | 5 w | N/A | N/A | Cauterized ES+OPC systemic 100 mg/kg group: 46.9±18.8% | V2 receptor antagonists |
| Degerman et al. [31] | Mice | VP at 50 mg/100 g/d for 14-30 d | 27 d | N/A | N/A | 1.4-fold increase (27 d in C57BL6 mice) | Compared by 9.4 T magnetic resonance imaging |
| 2-fold increase (14 d in CBA/J mice) | |||||||
| Katagiri et al. [32] | Mice | VP at a dose of 50 mg/100 g/d for 5 d-8 w | 5 d-8 w | N/A | N/A | Increased | Reversible vestibular dysfunction following intratympanic injection of epinephrine |
| Kitano et al. [42] | Rat | VP at the rate of 8 mU/kg/min for 1 w | 1 w | N/A | N/A | 5.9±7.1% in treated group vs. -0.2±2.6% in control | Light microscope with the increase ratio formula |
| Takeda et al. [9] | Guinea pig | VP at 0.57 or 1.14 or 2.86 ng/kg/min for 1 w | 1 w | N/A | N/A | Increased (1.14 or 2.86 ng/kg/min) | Light microscope with the increase ratio formula |
REFERENCES
1. Pearson WP, Brackmann DE. Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium: Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the diagnosis and evaluation of therapy in Meniere’s disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1995;113:181–5.


2. Oberman BS, Patel VA, Cureoglu S, Isildak H. The aetiopathologies of Ménière’s disease: a contemporary review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2017;37:250–63.


3. Salt AN, Plontke SK. Endolymphatic hydrops: pathophysiology and experimental models. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2010;43:971–83.



4. Brown DJ, Chihara Y, Curthoys IS, Wang Y, Bos M. Changes in cochlear function during acute endolymphatic hydrops development in guinea pigs. Hear Res 2013;296:96–106.

5. Kim M, Kim KS. Vestibular function change in a vasopressin-induced hydrops model. Otol Neurotol 2017;38:e495. –500.


6. Kimura RS, Schuknecht HF. Membranous hydrops in the inner ear of the guinea pig after obliteration of the endolymphatic sac. Pract Otorhinolaryngol (Basel) 1965;27:343–54.

7. Liu H, Zhou K, Zhang X, Peng KA. Fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss. Audiology and Neurotology 2019;24:109–16.


8. Kimura RS, Schuknecht HF. Effect of fistulae on endolymphatic hydrops. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1975;84(3 Pt 1):271–86.


9. Takeda T, Takeda S, Kitano H, Okada T, Kakigi A. Endolymphatic hydrops induced by chronic administration of vasopressin. Hear Res 2000;140:1–6.


10. Chihara Y, Wong C, Curthoys IS, Brown DJ. The effect of systemic administration of desmopressin on cochlear function in guinea pigs. Acta Otolaryngol 2013;133:676–84.


11. Tian Q, Linthicum FH Jr, Keithley EM. Application of labeling techniques to archival temporal bone sections. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1999;108:47–53.


12. Lopez IA, Ishiyama G, Hosokawa S, Hosokawa K, Acuna D, Linthicum FH, et al. Immunohistochemical techniques for the human inner ear. Histochem Cell Biol 2016;146:367–87.



13. Hofman R, Segenhout JM, Wit HP. A bast-like valve in the pigeon? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2009;266:1397–401.



14. Agrawal Y, Minor LB. Physiologic effects on the vestibular system in Meniere’s disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2010;43:985–93.


15. Derebery MJ. Allergic and immunologic features of Ménière’s disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2011;44:655–66.


16. Schuknecht HF, Gulya AJ. Endolymphatic hydrops: an overview and classification. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1983;92(5 Suppl):1–20.

17. Gibson WP. Hypothetical mechanism for vertigo in Meniere’s disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2010;43:1019–27.


18. Aoki M, Ando K, Kuze B, Mizuta K, Hayashi T, Ito Y. The association of antidiuretic hormone levels with an attack of Meniere’s disease. Clin Otolaryngol 2005;30:521–5.


19. Kitahara T, Doi K, Maekawa C, Kizawa K, Horii A, Kubo T, et al. Meniere’s attacks occur in the inner ear with excessive vasopressin type-2 receptors. J Neuroendocrinol 2008;20:1295–300.


20. Wangemann P, Liu J, Shimozono M, Schimanski S, Scofield MA. K+ secretion in strial marginal cells is stimulated via beta 1-adrenergic receptors but not via beta 2-adrenergic or vasopressin receptors. J Membr Biol 2000;175:191–202.

21. Derebery MJ, Berliner KI. Prevalence of allergy in Meniere’s disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;123(1 Pt 1):69–75.


23. Derebery MJ, Rao VS, Siglock TJ, Linthicum FH, Nelson RA. Menière’s disease: an immune complex-mediated illness? Laryngoscope 1991;101:225–9.

24. Brown DJ, Sokolic L, Fung A, Pastras CJ. Response of the inner ear to lipopolysaccharide introduced directly into scala media. Hear Res 2018;370:105–12.


25. Fung K, Xie Y, Hall SF, Lillicrap DP, Taylor SA. Genetic basis of familial Meniere’s disease. J Otolaryngol 2002;31:1–4.


26. Teggi R, Lanzani C, Zagato L, Delli Carpini S, Manunta P, Bianchi G, et al. Gly460Trp alpha-adducin mutation as a possible mechanism leading to endolymphatic hydrops in Ménière’s syndrome. Otol Neurotol 2008;29:824–8.


27. Lopez-Escamez JA, Saenz-Lopez P, Acosta L, Moreno A, Gazquez I, Perez-Garrigues H, et al. Association of a functional polymorphism of PTPN22 encoding a lymphoid protein phosphatase in bilateral Meniere’s disease. Laryngoscope 2010;120:103–7.


28. Dunnebier EA, Segenhout JM, Wit HP, Albers FW. Two-phase endolymphatic hydrops: a new dynamic guinea pig model. Acta Otolaryngol 1997;117:13–9.


29. Egami N, Kakigi A, Sakamoto T, Takeda T, Hyodo M, Yamasoba T. Morphological and functional changes in a new animal model of Ménière’s disease. Lab Invest 2013;93:1001–11.


30. Egami N, Kakigi A, Takeda T, Yamasoba T. Dehydration effects of a V2 antagonist on endolymphatic hydrops in guinea pigs. Hear Res 2016;332:151–9.


31. Vasopressin induces endolymphatic hydrops in mouse inner ear, as evaluated with repeated 9. 4 T MRI. Hear Res 2015;330(Pt A):119–24.


32. Katagiri Y, Takumida M, Hirakawa K, Anniko M. Long-term administration of vasopressin can cause Ménière’s disease in mice. Acta Otolaryngol 2014;134:990–1004.


33. Francis F, Hennig S, Korn B, Reinhardt R, De Jong P, Poustka A, et al. A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases is mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Nat Genet 1995;11:130–6.


34. Megerian CA, Semaan MT, Aftab S, Kisley LB, Zheng QY, Pawlowski KS, et al. A mouse model with postnatal endolymphatic hydrops and hearing loss. Hear Res 2008;237:90–105.



35. Sheykholeslami K, Megerian CA, Zheng QY. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in normal mice and Phex mice with spontaneous endolymphatic hydrops. Otol Neurotol 2009;30:535–44.



36. Wick CC, Semaan MT, Zheng QY, Megerian CA. A genetic murine model of endolymphatic hydrops: the Phex mouse. Curr Otorhinolaryngol Rep 2014;2:144–51.



37. Ingham NJ, Thornton SK, Comis SD, Withington DJ. The auditory brainstem response of aged guinea pigs. Acta Otolaryngol 1998;118:673–80.


38. Sirjani DB, Salt AN, Gill RM, Hale SA. The influence of transducer operating point on distortion generation in the cochlea. J Acoust Soc Am 2004;115:1219–29.


39. Valk WL, Wit HP, Albers FW. Evaluation of cochlear function in an acute endolymphatic hydrops model in the guinea pig by measuring low-level DPOAEs. Hear Res 2004;192:47–56.

40. Campbell KC, Faloon KM, Rybak LP. Noninvasive electrodes for electrocochleography in the chinchilla. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1993;119:767–71.